
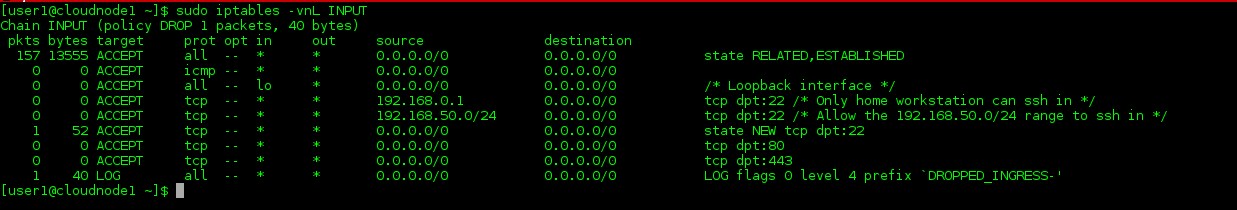
ctstate - Define the list of states for the rule to match on. m conntrack - Allow filter rules to match based on connection state. Valid chains for what we're doing are INPUT, FORWARD and OUTPUT, but we mostly deal with INPUT in this tutorial, which affects only incoming traffic. Don't worry about understanding everything here now, but remember to come back and look at this list as you encounter new options later on. Here are explanations for some of the iptables options you will see in this tutorial. If you have just set up your server, you will have no rules, and you should see Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT) There is a wealth of information available about iptables, but much of it is fairly complex, and if you want to do a few basic things, this How To is for you. Ubuntu comes with ufw - a program for managing the iptables firewall easily. When you install Ubuntu, iptables is there, but it allows all traffic by default. Iptables is a firewall, installed by default on all official Ubuntu distributions (Ubuntu, Kubuntu, Xubuntu).

Solution #2 /etc/network/if-pre-up.d and.Allowing Incoming Traffic on Specific Ports.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
